Diving into the relationship between ‘Elderberry and Zoloft’? While Elderberry is cherished in both traditional and Ayurvedic medicine for its immune-boosting properties, it’s crucial to note its potential interactions. Avoid pairing Elderberry with immunosuppressants. For efficient relief from cold and flu, explore other natural cold remedies.
Benefits
Elderberry is an ancient folk remedy and has been in use for centuries. Historically, elderberry was employed as an immune booster and to prevent colds and flu; more recently however it may also reduce high blood pressure, improve cardiovascular health and protect against cell damage; it can even treat sinusitis and bronchitis! Elderberry syrup, juice or tea products can be purchased in most health food stores; you can even make your own by boiling fresh berries and stems with water before adding lemon.
Anthocyanins and flavonoids found in this plant provide several skin health advantages, including improving wrinkles, crow’s feet, as well as treating dark spots and keeping your skin hydrated with essential hydration for maintaining an attractive glow. Because of this herb’s many health benefits it has made its way into many cosmetic products and many skincare regimens.
Elderberry can be used as a natural diuretic, encouraging both urination and bowel movements to help combat fluid retention. When combined with herbal products it can also treat constipation; further research suggests it can even protect against oxidative stress.
Sambucus nigra, commonly referred to as the black elder plant, can be found throughout Europe and parts of Africa and Asia. It features deciduous leaves with white elderflower flowers (elderflowers) as well as dark-green to red-black berries packed with antioxidants; though these berries are edible when cooked they should be avoided due to cyanide poisoning risk.
Elderberry offers impressive health benefits; however, certain autoimmune disorders should avoid using it due to its presumed effect of increasing immune activity – this could make distinguishing between healthy cells and those associated with an autoimmune disease more challenging. Furthermore, elderberry may interact negatively with certain prescription medications.
Side effects
Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is an increasingly popular over-the-counter supplement due to its immune-enhancing benefits. It is frequently combined with vitamin C and zinc and found in products like syrups, gummies, and supplements; and has proven effective against colds, flus, sinusitis, and other upper respiratory infections as well as helping reduce oxidative stress levels while improving heart health.
Elderberry supplements do not pose any known severe or serious side effects; however, certain interactions may reduce or increase their effectiveness and thus it is wise to seek advice from healthcare providers before adding new supplements into your regimen.
Elderberry was found to be effective at lowering cholesterol and decreasing oxidative damage to cells, according to one small study; however, more research needs to be conducted in order to confirm these results and replicate them. Furthermore, pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, those suffering from bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulants should avoid taking elderberry for these reasons.
Be mindful of any possible allergic reactions when taking elderberry. The berries contain compounds which could potentially trigger nausea and vomiting if taken improperly, so if any symptoms appear seek medical help immediately.
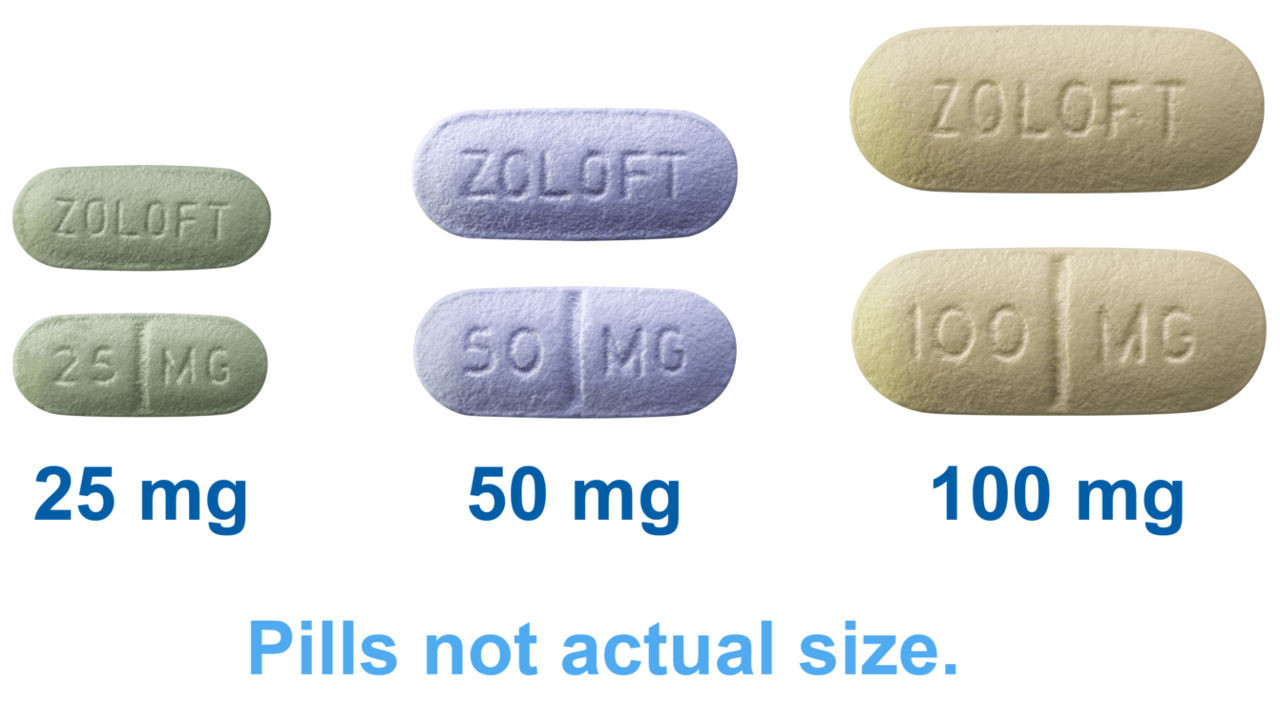
Zoloft side effects may not be common, but should they occur it’s important to notify your physician as soon as possible. If any of the following symptoms appear contact your physician immediately:
Noting the potential interaction of dietary supplements with Zoloft, such as herbs that increase serotonin levels if taken with an SSRI such as Zoloft could prove dangerous. Avoid herbal products containing 5-HT and L-tryptophan as precursors for serotonin production; taking these with Zoloft increases the risk of serotonin syndrome – which could prove serious and even fatal – so inform your physician if taking additional herbs or dietary supplements that might interact.
Interactions
Elderberries are an over-the-counter herbal remedy commonly used to treat colds, yet there’s no evidence they interact negatively with Zoloft, providing they are taken according to doctor prescription. Elderberry can reduce stress levels and boost immune systems – two qualities which could help you avoid contracting an illness altogether.
Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is an herbaceous shrub with dark purple or black berries that has long been used as an antiviral and immune-stimulating supplement. Elderberries boast numerous nutritional and therapeutic properties that make it suitable for antidepressant use as well. Their beneficial effects include antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and antidepressant activities; plus rich sources of vitamins C and other important B vitamins such as fibre. Phytochemicals provide additional health benefits of their plant source as well as various nutrients that the fruit provides.
This randomized controlled trial involved 312 participants taking either elderberry capsules or placebo for 10 days prior to an international long-haul flight and four days afterward. They kept a diary to record symptoms as well as completed three quality of life surveys that included WURSS-21 and SF-12 scores at three separate time points.
This study revealed that elderberry significantly decreased both the frequency and duration of cold episodes, with elderberry preparations providing the strongest evidence yet of effective travel-related cold symptom reduction with its preventive interventions.
Elderberry was generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events reported, though five participants experienced itchy throat or cold-like symptoms due to its high anthocyanin content. Researchers used the PSS scale to identify these individuals because those experiencing more stress tend to experience an increase in cold symptoms despite no causal connection being made between elderberry consumption and these effects.
Although the results of this study were encouraging, there are a few key limitations to take into account. First, participants in this study were highly stressed – an often contributing factor for colds which can be worsened by long-haul flights and time changes during travel. Therefore, further investigation must be conducted into elderberry as an effective treatment to mitigate symptoms among travellers.
Precautions
Elderberry benefits may cause certain side effects that should be taken into consideration before beginning use. Most people can safely consume this natural remedy without experiencing adverse reactions; however, before adding any supplements or herbs into your diet. Here are some of the more frequently reported side effects:
American elderberry (Sambucus canadensis) and black elderberry (Sambucus nigra) have long been used as medicinal remedies, with the latter variety most frequently seen as part of dietary supplements due to its stronger flavor than its counterpart variety. Both varieties should be safe to consume but are typically only found as black elderberries due to being more commonly available commercially than its American elder counterparts.
American Elder and Black Elderberry contain compounds that act as laxatives, so it is wise to avoid taking these berries with other laxatives as this could create dangerous side effects. Furthermore, pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should refrain from eating American or Black Elderberries due to the nutrients found within these berries that could harm an unborn or nursing infant.
Elderberry can help reduce blood sugar levels. However, taking it with diabetes medications could increase your risk of low blood sugar, potentially leading to dangerously low levels. Therefore it is wise to consult your healthcare provider prior to adding elderberry into your diet if you are already taking diabetes medications.
Elderberry can not only reduce blood sugar levels, but is also believed to aid with digestion, reduce flu symptoms and alleviate arthritis pain. Furthermore, elderberry serves as an immune booster and forms part of traditional Ayurvedic medicine practices.
Elderberry is generally safe when taken in moderation and does not interact with most medications; however, it should not be given to people suffering from certain autoimmune disorders as this could increase immunity and worsen symptoms of their conditions. Furthermore, immunosuppressant drugs reduce activity within the immune system so this natural medicine should not be combined.